low end tidal co2 pulmonary embolism
We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO 2 etCO 2 and tested two hypotheses. 1 that etCO 2 can distinguish massive PE from hemorrhagic shock and 2 that PE with cardiac arrest reduces etCO 2 during resuscitation to a greater extent than arrhythmic cardiac arrest.

Pre Hospital Capnography Ppt Download
If there was no alveolar dead space end-tidal CO 2 would be identical to alveolar CO 2.

. Predictive Value of Tests. All patients positive for. Continuous pulmonary arterial pressure can be used to evaluate for gas embolism.
1 CO2 embolism can occur from the accidental intravascular injection of CO2 which may arise from the inappropriate placement of the Veress needle within the intravascular space. Massive pulmonary embolism PE results in low CO2 transport due to hemodynamic compromise together with an alveolar. Increased alveolar to arterial oxygen.
11098986 PubMed - indexed for. Pulmonary embolism PE is associated with approximately 100000 deaths per year in the United States and the incidence of deep vein thrombosispulmonary embolism in the United States is estimated at more than 350000 cases annually. End-tidal CO2 ETCO 2 can represent dead space ventilation.
Request PDF A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism Introduction. Carbon Dioxideblood Critical Care. PE was diagnosed in 38 of cases.
1 The diagnosis of pulmonary embolism poses a diagnostic challenge in the emergency department ED despite validated. 298 patients were enrolled over 6 months at a single academic centre. 479 consecutive patients with suspected PEs were enrolled over 3 years in 2012-2014 and 2019.
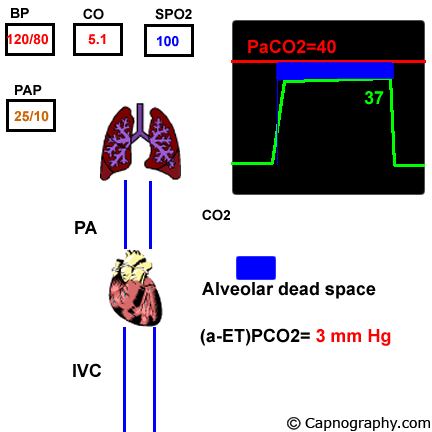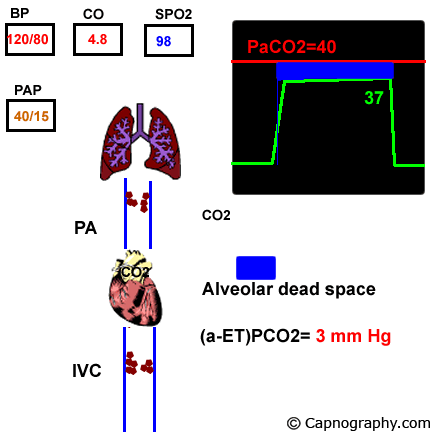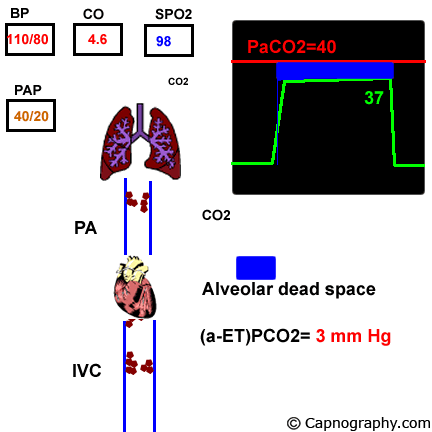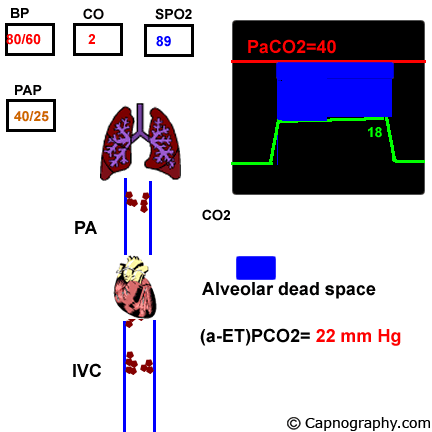
----- malfunction can also affect EtCO2. A similar mechanism is possible with trocar insertion. Pulmonary embolism increases alveolar dead space resulting in low end-tidal CO 2 EtCO 2 relative to arterial CO 2 PaCO 2 tensionThus a low EtCO 2 PaCO 2 ratio during resuscitation may be a sign of pulmonary embolism.
A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project Evaluation Of Suspected Pulmonary Embolism Utilizing End Tidal Co2 And D Dimer The American Journal Of Surgery. Sudden decrease or loss of end-tidal CO2 suggests a drastic decrease in cardiac output due to gas embolism. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO2 etCO2 and tested two hypotheses.
What happens to CO2 in pulmonary embolism. Potential Gas Exchange Abnormalities in Pulmonary Embolism. We aimed to define the optimal P ETCO2 level to exclude PE in patients evaluated for possible thromboembolism.
ArticleAagaard2018ALE titleA low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism authorRasmus Aagaard and Bo Lofgren. 2 CO2 embolism can also result from gas. Pulmonary thromboembolism results in dead space ventilation and therefore prevents meaningful gas exchange in the subtended lung unit yielding an alveolar CO2 content as low as 0 mmHg.
Pulmonary Embolismdrug therapy Recurrence. Management of a suspected CO2 embolism begins with desufflation of the abdomen. Known as the arterial-to-etco2 gradient this differential results from small amounts of dead-space ventilation ventilation without perfusion and a slight venous admixture.
We aimed to define the optimum ETCO 2 to exclude a pulmonary emboli PE event conclusively. Decreased arterial P o 2. Identifying reversible causes of cardiac arrest is challenging.
Two possible mechanisms can explain the pathophysiology of CO2 embolism. We investigated the effect of massive pulmonary embolism MPE on end tidal CO 2 etCO 2 and tested two hypotheses. Causes of changes in end-tidal CO2 can be divided into changes in CO2 production impaired pulmonary perfusion andor impaired ventilation.
Alveolar dead space contain a gas mixture which is identical to. Normal PaCO 2 -EtCO 2 difference is 2-5 mmHg Satoh et al 2015 This is due to alveolar dead space which is small in healthy adults. In a state of perfect equilibrium arterial and end-tidal CO 2 levels correlate on a 11 basis.
End tidal carbon dioxide tension P ETCO2 is a surrogate for dead space ventilation which may be useful in the evaluation of pulmonary embolism PE. The average ETCO 2 in patients with a positive CTPA was 335 kPa range 2442 kPa SD 050. The average ETCO 2 in patients without a PE was 441 kPa range 1366 kPa SD 110.
A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism. Alveoli which are ventilated but not perfused ie. 1 that etCO 2 can distinguish massive PE from hemorrhagic shock and 2 that PE with cardiac arrest reduces etCO 2 during resuscitation to a greater extent than arrhythmic cardiac arrest.
Comment on Crit Care Med. But even in an ideal physiologic state a difference of 2 to 5 mm Hg usually exists. Bøtker M and Granfeldt A 2018 A low end-tidal CO2arterial CO2 ratio during cardiopulmonary resuscitation suggests pulmonary embolism Resuscitation 101016jresuscitation201810008 133 137-140.
A new niche for end-tidal CO2 in pulmonary embolism.

Capnography And Pulmonary Embolism Chapter 21 Capnography
5 Medical Conditions Where Capnography Can Affect Bls Care Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

A Low End Tidal Co2 Arterial Co2 Ratio During Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation Suggests Pulmonary Embolism Resuscitation

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Different Capnography Traces A Sudden Drop In E 0 Co2 B Download Scientific Diagram

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Basic Capnography Interpretation Nuem Blog

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Basics Of Waveform Capnography Waveform Capnography Grepmed

Capnography Provides Bigger Physiological Picture To Maximize Patient Care Jems Ems Emergency Medical Services Training Paramedic Emt News
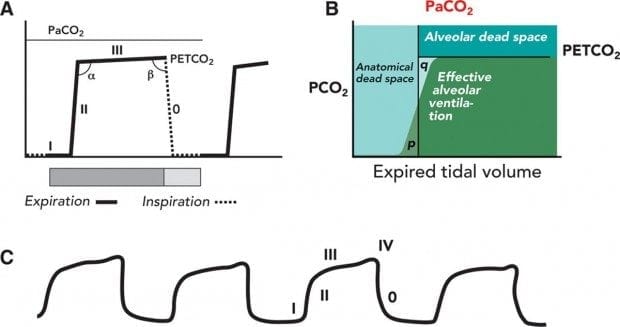
Capnography Waveform Interpretation Litfl Ccc Equipment

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project

Pulmonary Embolism Alters Alveolar Dead Space And End Tidal Carbon Download Scientific Diagram

Waveform Capnography In The Intubated Patient Emcrit Project